Docker is a powerful containerization platform that simplifies application deployment and management by packaging them with their dependencies. It allows developers and system administrators to create lightweight, portable, and consistent environments.
In this guide, we will walk you through installing Docker on Ubuntu 24.04 and show you how to use it to run containers.
Understanding IAM PassRole to Secure Your AWS Infrastructure
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
- A system running Ubuntu 24.04
- A user account with sudo privileges
- An active internet connection
Step 1: Update the System
Before installing Docker, update the package lists and upgrade existing packages:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -yThis ensures that all software on your system is up to date.
Step 2: Install Required Dependencies
Docker requires a few additional packages to function properly. Install them using:
sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-releaseThese packages help in managing secure connections and fetching necessary repositories.
Step 3: Add Docker’s Official GPG Key
Docker is not included in the default Ubuntu repositories, so we need to add its official GPG key for verification:
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.ascThis step ensures that the Docker packages we install are authentic and secure.
Step 4: Add the Docker Repository
Now, add the Docker repository to your system’s package sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullAfter adding the repository, update the package list:
sudo apt-get updateStep 5: Install Docker Engine
Now, install Docker and its related components:
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginOnce the installation is complete, check the Docker version to verify:
docker --versionThis should output something like:
Docker version 28.0.1, build 068a01e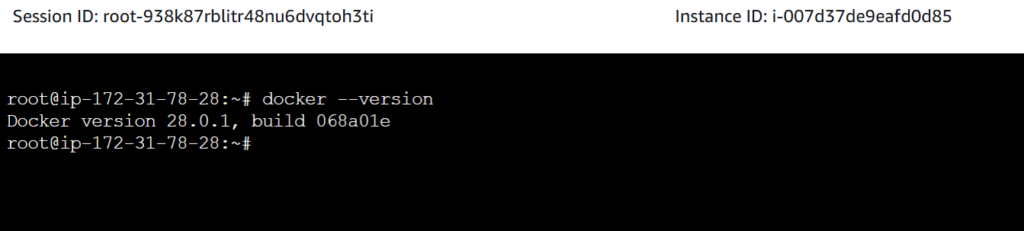
Step 6: Start and Enable Docker
Ensure that Docker is running and enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable dockerTo verify that Docker is running, use:
sudo systemctl status dockerYou should see an output indicating that Docker is active and running if everything is correct.

Step 7: Add Your User to the Docker Group (Optional)
By default, running Docker commands requires sudo privileges. To allow your user to run Docker without sudo, add it to the docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERStep 8: Basic Docker Commands
Now that Docker is installed, let’s explore some basic commands.
| Check the Installed Docker Version |
| docker –version |
| List Running Containers |
| docker ps |
| List All Containers (Including Stopped Ones) |
| docker ps -a |
| Run a Test Container |
| docker run hello-world |
| Pull an Image from the Docker Hub |
| docker pull ubuntu |
| Run a Container in Interactive Mode |
| docker run -it ubuntu /bin/bash |
| Stop a Running Container |
| docker stop <container_id> |
| Remove a Stopped Container |
| docker rm <container_id> |
| Remove an Image |
| docker rmi <image_id> |
| Remove All Unused Images, Containers, and Networks |
| docker system prune -a |
Uninstalling Docker (If Needed)
If you ever need to uninstall Docker, use the following command:
sudo apt remove -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginTo remove all Docker data, including images and containers, run:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker