Hi Techies,
In this blog, you will learn What is the difference between AWS Direct Connect and Site-to-Site VPN (Virtual Private Network). Before starting, ensure you know about all AWS networking services and their uses.
Before comparison, let understand what is Site-to-Site VPN and AWS Direct Connect.
What is AWS Site-to-Site VPN?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Site-to-Site VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a network connectivity solution that allows you to establish a secure and encrypted connection between your on-premises network infrastructure and your virtual private cloud (VPC) environments within AWS.
This type of VPN connection enables you to extend your on-premises network into the AWS cloud, creating a hybrid architecture that combines the resources and capabilities of both environments.
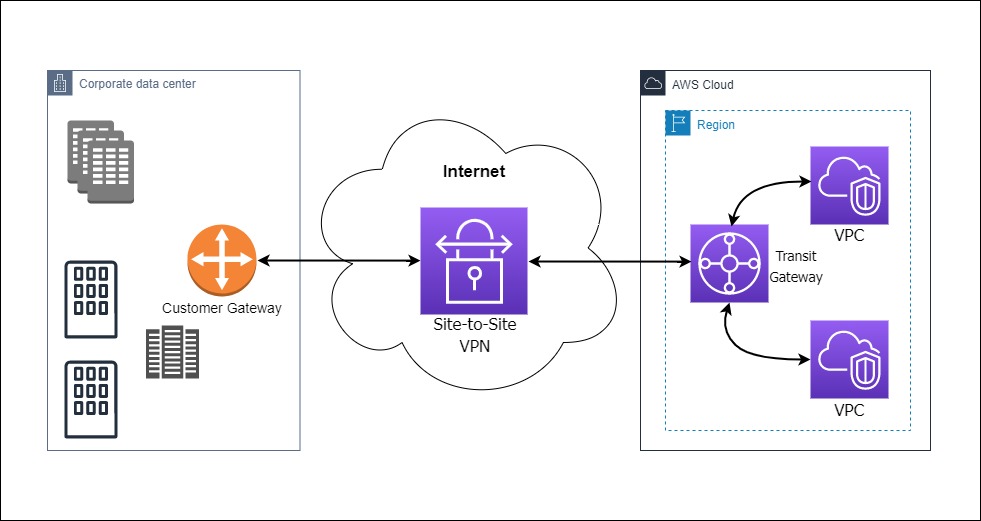
Key features of AWS Site-to-Site VPN
- Secure Communication: Site-to-Site VPN establishes encrypted tunnels over the public internet, ensuring that data transmitted between your on-premises network and your AWS resources remains secure and confidential.
- IPsec Encryption: The VPN connection uses IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) protocols to provide authentication and encryption for data in transit. This helps prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping on your data.
- Hybrid Cloud Connectivity: Site-to-Site VPN enables you to create hybrid cloud architectures by extending your on-premises network into your AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). This facilitates seamless communication and resource sharing between your local network and your AWS environment.
- Network Isolation: You can set up separate VPCs with isolated network environments and connect them to your on-premises network using individual VPN connections. This allows you to maintain segmentation and isolation between different application workloads.
- Routing Control: You have control over the routing tables for your VPN connection on both the AWS side and your on-premises side. This flexibility allows you to define how traffic flows between your networks.
- Scalability: AWS Site-to-Site VPN supports multiple VPN connections, making it suitable for scenarios where you need to connect multiple on-premises locations to your AWS resources.
- Redundancy: You can configure redundant Site-to-Site VPN connections to enhance availability and failover capabilities. If one connection becomes unavailable, traffic can automatically fail over to the backup connection.
- Multi-Region Support: You can set up Site-to-Site VPN connections to different AWS regions, allowing you to establish network connectivity across geographically dispersed AWS environments.
- Ease of Management: AWS Management Console provides a user-friendly interface for configuring and managing your Site-to-Site VPN connections, making it relatively straightforward to set up and monitor your connections.
- Cost Control: AWS charges for Site-to-Site VPN connections based on usage, making it cost-effective for smaller-scale deployments or situations where budget is a consideration.
- Remote Access: Site-to-Site VPN can also be used to provide remote access for users connecting from outside your on-premises network. This is useful for securely accessing resources within your VPC.
- Compatibility: Site-to-Site VPN is compatible with a wide range of networking equipment, allowing you to establish connections using standard VPN protocols and devices.
AWS Site-to-Site VPN is particularly useful for scenarios where you need to extend your on-premises network to the cloud. This could be for purposes such as disaster recovery, data center migration, remote access, or resource sharing between on-premises and cloud environments. It provides a secure and reliable way to connect your networks without exposing sensitive data to the public internet.
What is AWS Direct Connect?
AWS Direct Connect is a network service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables you to establish a dedicated and private network connection between your on-premises data center, office, or colocation facility, and AWS. Unlike a virtual private network (VPN) that operates over the public internet, AWS Direct Connect offers a more reliable, consistent, and higher-bandwidth connection to the AWS cloud.
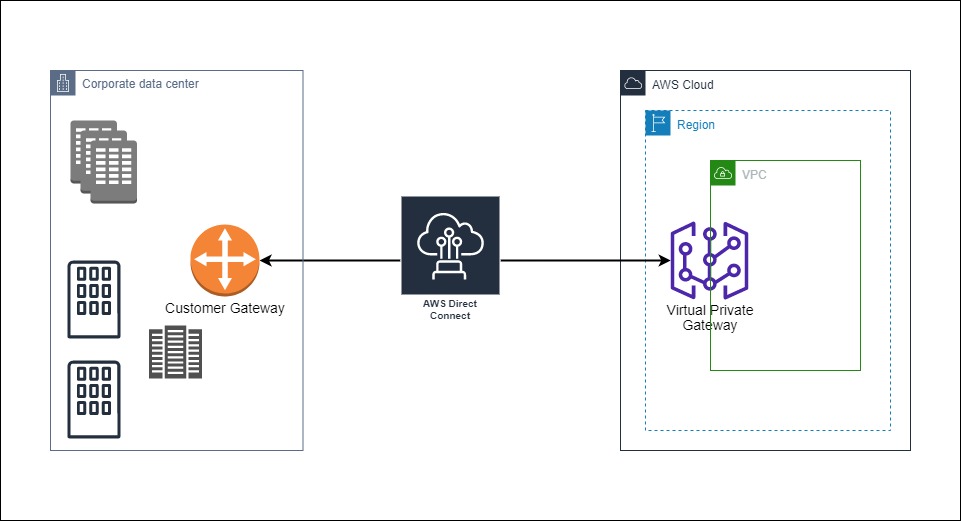
Key features and aspects of AWS Direct Connect include:
- Dedicated Connection: With AWS Direct Connect, you can set up a dedicated physical connection between your network and AWS. This connection is established through a Direct Connect location, which can be an AWS Direct Connect partner facility or an AWS-owned location.
- Private and Secure: The connection between your network and AWS is private and bypasses the public internet. This enhances security and can be particularly important for transmitting sensitive or confidential data.
- Higher Bandwidth: Direct Connect connections can provide higher bandwidth compared to typical VPN connections. You can choose the speed of the connection based on your needs, ranging from 50 Mbps up to 100 Gbps.
- Reduced Latency: Since the connection is dedicated and private, it generally offers lower latency compared to a VPN connection over the public internet. This can be crucial for applications that require real-time or low-latency communication.
- Predictable Performance: The dedicated nature of the connection ensures consistent and predictable performance, making it suitable for scenarios where data transfer speed and reliability are critical.
- Hybrid Architectures: AWS Direct Connect is often used to establish hybrid cloud architectures, where resources in your on-premises network seamlessly interact with resources in your AWS environment. This is useful for scenarios such as data migration, disaster recovery, and hybrid application deployments.
- Virtual Interfaces: Within your Direct Connect connection, you can create virtual interfaces that allow you to connect to multiple Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) or other AWS services within the same region.
- Resilience and Redundancy: AWS Direct Connect can be configured for redundancy, providing additional reliability by setting up multiple connections across different locations or through different partners.
Difference between AWS site-to-site VPN and AWS Direct Connect
AWS Site-to-Site VPN and AWS Direct Connect are both network connectivity solutions that allow you to establish connections between your on-premises network and your AWS resources. However, they differ in terms of their underlying technology, use cases, features, and benefits. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between AWS Site-to-Site VPN and AWS Direct Connect:
- Underlying Technology:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Utilizes IPsec tunnels over the public internet to create a secure and encrypted connection between your on-premises network and AWS resources.
- Direct Connect: Establishes a dedicated physical connection between your network and AWS using a private network connection.
- Connection Type:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Connection is established over the public internet, making it suitable for scenarios where security and data privacy are important but not as high as with dedicated connections.
- Direct Connect: The connection is private and dedicated, offering a higher level of security and reliability compared to VPNs.
- Bandwidth and Latency:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Typically offers lower bandwidth and potentially higher latency due to the variability of internet traffic.
- Direct Connect: Offers higher bandwidth options and generally lower latency due to the dedicated nature of the connection.
- Predictable Performance:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Performance can vary based on internet traffic and network conditions.
- Direct Connect: Provides consistent and predictable performance, making it suitable for applications requiring low latency and high throughput.
- Security:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Offers encryption for data transmission but relies on the public internet, which might be subject to security risks.
- Direct Connect: Offers a more secure option by establishing a private connection that bypasses the public internet.
- Use Cases:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Often used for remote access, small-scale hybrid architectures, or scenarios where cost is a major consideration.
- Direct Connect: Suited for large-scale hybrid architectures, data migration, disaster recovery, applications requiring low latency, and situations where security and performance are critical.
- Redundancy and Resilience:
- Site-to-Site VPN: This can be configured for redundancy using multiple VPN connections, but failover might take longer.
- Direct Connect: Offers built-in redundancy and failover options for enhanced reliability.
- Configuration Complexity:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Generally simpler to set up and manage, especially for smaller deployments.
- Direct Connect: Involves more complex setup, coordination with partners or AWS-owned locations, and the deployment of networking equipment.
- Cost:
- Site-to-Site VPN: Typically has lower setup costs and is billed based on data transfer and VPN connection hours.
- Direct Connect: Generally involves higher setup costs, including cross-connect fees and ongoing port charges, but might be more cost-effective for higher data transfer volumes.
In summary, AWS Site-to-Site VPN is a suitable choice for scenarios where security is important and budget constraints are a consideration. AWS Direct Connect is preferable when reliability, performance, low latency, and security are critical requirements, and when you need a dedicated, private connection to your AWS resources. The choice between the two depends on your organization’s specific networking needs and priorities.