AWS Landing Zone Overview
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers AWS Landing Zone as a solution to assist customers in establishing a secure, multi-account AWS environment based on AWS best practices.
It provides a foundation for deploying and managing AWS workloads in a well-architected and secure manner.
It’s designed to accelerate the adoption of AWS by streamlining the setup process and ensuring that workloads are built on a secure and compliant foundation.
AWS Landing Zone Architecture
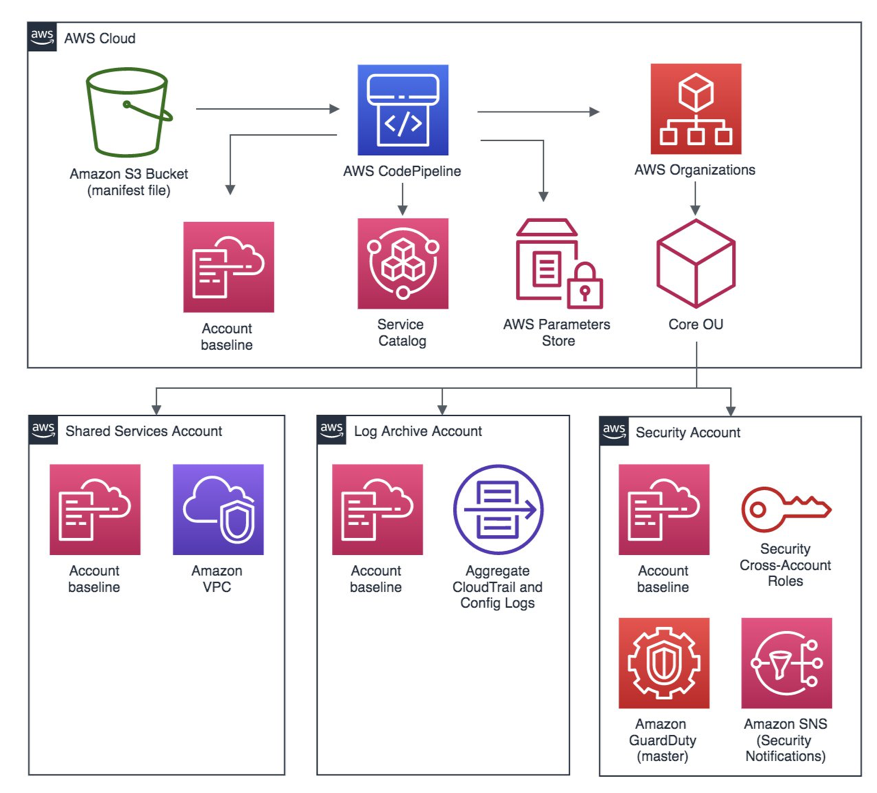
AWS Landing Zone solutions are commonly structured with four accounts.
- Master Account In the context of AWS Landing Zone, the term “Master Account” typically refers to the primary AWS account used for setting up and managing the Landing Zone environment. This account plays a central role in the AWS organization’s structure and is often associated with administrative responsibilities.
- Shared Services refers to a dedicated AWS account that hosts common services and resources shared across multiple accounts within an organization. The primary purpose of this account is to centralize certain AWS services and infrastructure components that are used collectively by other accounts within the Landing Zone architecture.
- Log Archive Account is an AWS account specifically dedicated to the centralized collection and storage of logs generated by various accounts within the Landing Zone environment. This account is designed to aggregate logs from multiple AWS accounts, providing a centralized location for auditing, compliance, and troubleshooting purposes.
- Security Account is a dedicated AWS account that plays a crucial role in ensuring the overall security and compliance of the AWS environment. This account is specifically designed to centralize security-related services, controls, and monitoring mechanisms
Key features of AWS Landing Zone
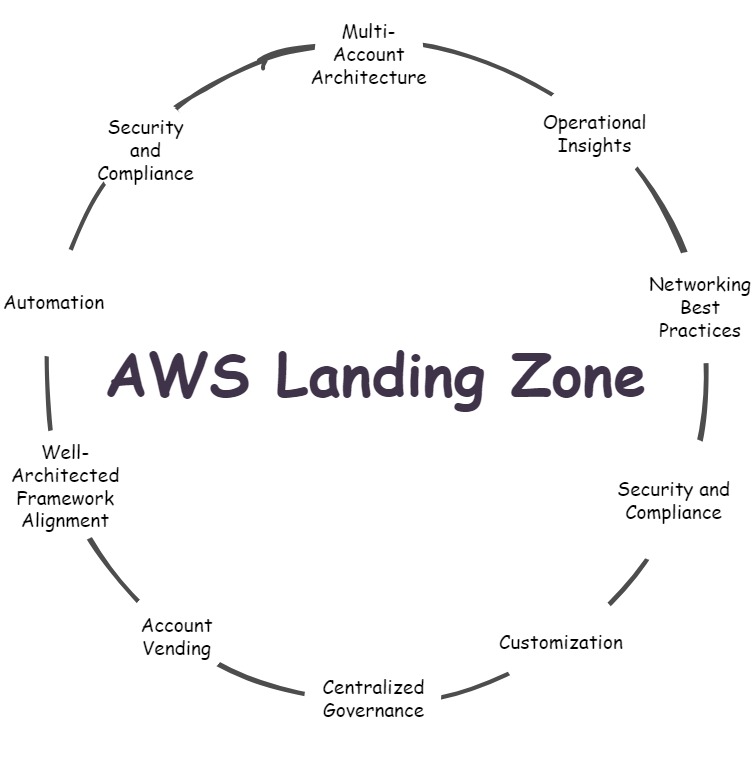
1. Multi-Account Architecture:
Purpose: Enables organizations to use multiple AWS accounts for better isolation, resource management, and security.
Benefits: Provides a structured approach to organizing workloads, allowing for segmentation based on projects, teams, or departments.
2. Security and Compliance:
Purpose: Implements AWS security best practices and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements.
Benefits: Ensures a strong security posture by incorporating identity and access management (IAM), network security, encryption, and compliance monitoring.
3. Automation:
Purpose: Automates the provisioning and configuration of AWS resources.
Benefits: Reduces manual errors, accelerates deployment, and ensures consistency in resource setups across accounts.
4. Well-Architected Framework Alignment:
Purpose: Aligns with the AWS Well-Architected Framework, covering pillars such as operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, and cost optimization.
Benefits: Ensures that workloads are designed and operated according to best practices, promoting efficiency, resilience, and cost-effectiveness.
5. Account Vending:
Purpose: Provides a mechanism for creating new accounts based on predefined templates.
Benefits: Facilitates scalability by streamlining the process of adding new accounts as the organization grows or new projects are initiated.
6. Centralized Governance with AWS Organizations:
Purpose: Integrates with AWS Organizations to centrally manage and govern multiple AWS accounts.
Benefits: Enables centralized control over policies, access management, and resource usage across the organization.
7. Customization:
Purpose: Allows organizations to customize the AWS Landing Zone setup based on their specific requirements.
Benefits: Provides flexibility to adapt the solution to unique organizational needs while maintaining a standardized foundation.
8. Security and Compliance Baseline:
Purpose: Establishes a baseline of security and compliance controls across all accounts.
Benefits: Ensures a consistent and secure starting point for all workloads, reducing the risk of misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
9. Networking Best Practices:
Purpose: Implements networking best practices for a well-architected and secure network infrastructure.
Benefits: Optimizes network design for performance, security, and reliability.
10. Operational Insights:
Purpose: Provides tools and insights for monitoring, logging, and operational excellence.
Benefits: Facilitates effective operations by offering visibility into the performance and health of AWS workloads.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive notifications about the next part of our articles. Don’t miss out on the latest updates and insights. Simply click the link below to subscribe.






