Hello Friends,
Today, we will discuss about “what is the difference between AWS transit gateway and VPC peering”. This is most important topic for any cloud engineers and commonly asked in the interviews.
So, first we need to understand, what is the purpose of AWS Transit Gateway and VPC Peering? The answer is both Transit Gateway and VPC Peering are used to connect multiple VPC’s.
VPC Peering
- Networking connections between two VPCs.
- Two VPC’s could be in the Same or different AWS accounts.
- Low Cost since you need to pay only for data transfer.
- There is no any bandwidth limitation.
- No transit routing (see detail below).
- Complex at scale,
- Maximum 125 connections per VPC.
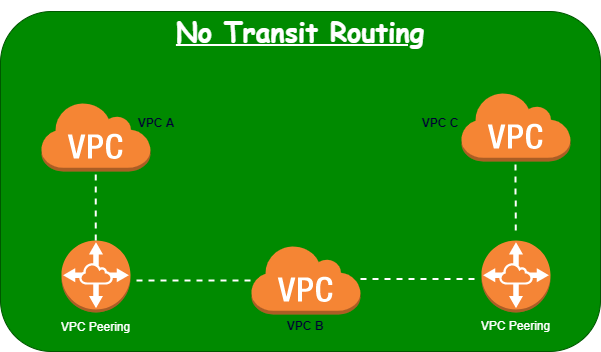
No Transit Routing
To understand the concept of NO Transit routing, we will take three VPC i.e. VPC A, VPC B & VPC C. Let suppose, we have a VPC Peering connection between VPC A and VPC B, and another between VPC B and VPC C, there is no VPC Peering connection (transitive peering) between VPC A and VPC C. This means we cannot communicate directly from VPC A to VPC C through VPC B and vice versa. Due to this lack of transitive peering in VPC Peering, AWS introduces concept of AWS Transit Gateway.
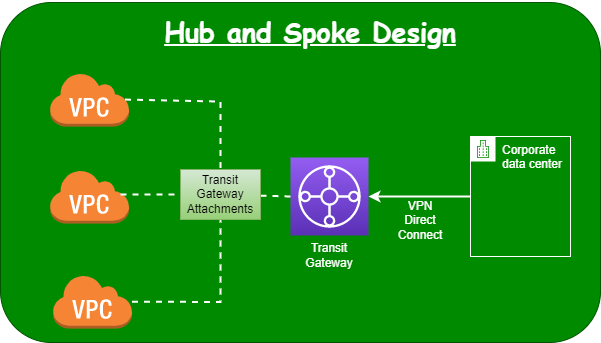
Transit Gateway
AWS Transit Gateway is a fully managed service that connects VPCs and On-Premises networks through a central hub without relying on numerous point-to-point connections or Transit VPC.
- Using Transit Gateway, you can manage multiple connections very easily.
- AWS manages the auto scaling and availability needs.
- Supported 1000’s of connections.
- There is an extra hourly charge per attachments in addition to data fees, which makes transit gateway configuration costly.
- Max bandwidth burst to 50 Gbps.
- Transit Gateway peering only possible across regions, not within region.
- Hub and spoke network topology for connecting VPC together.